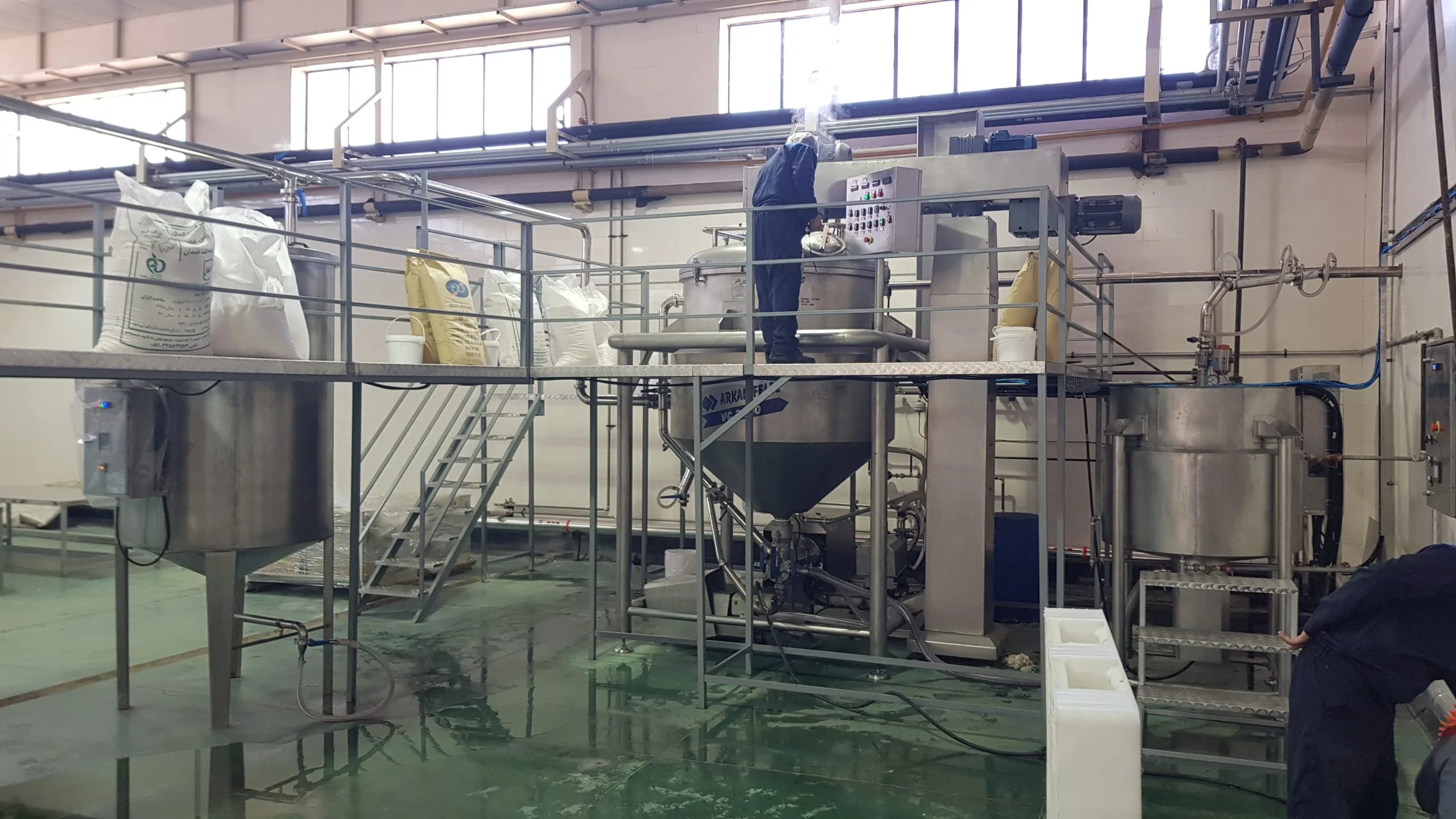
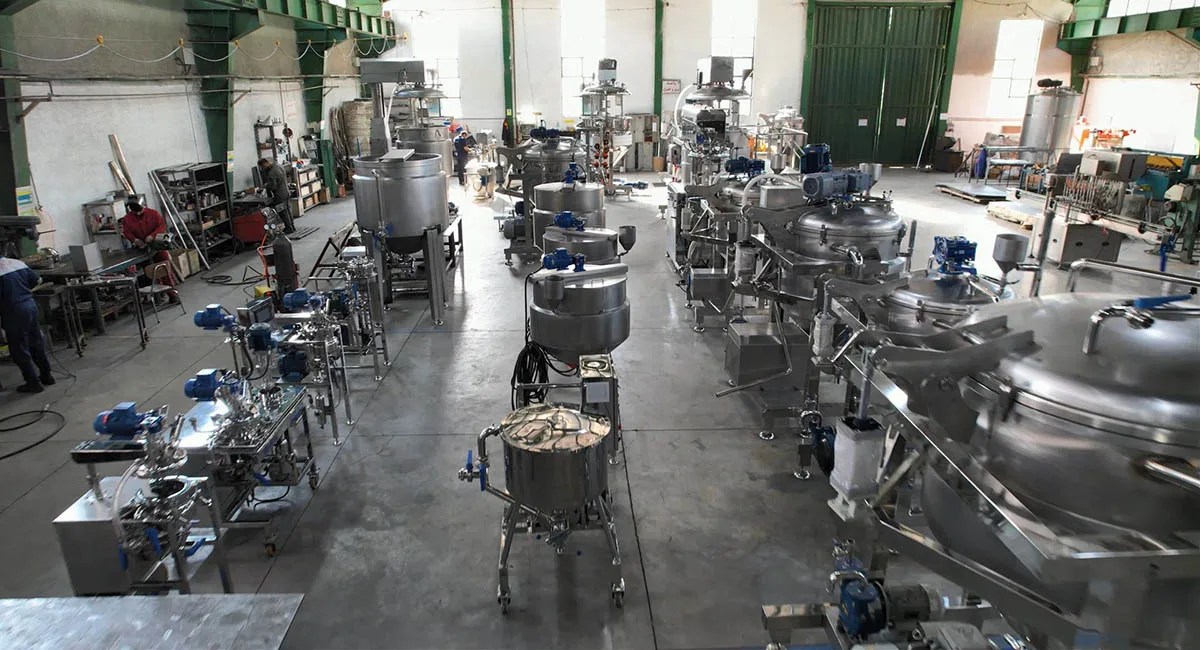
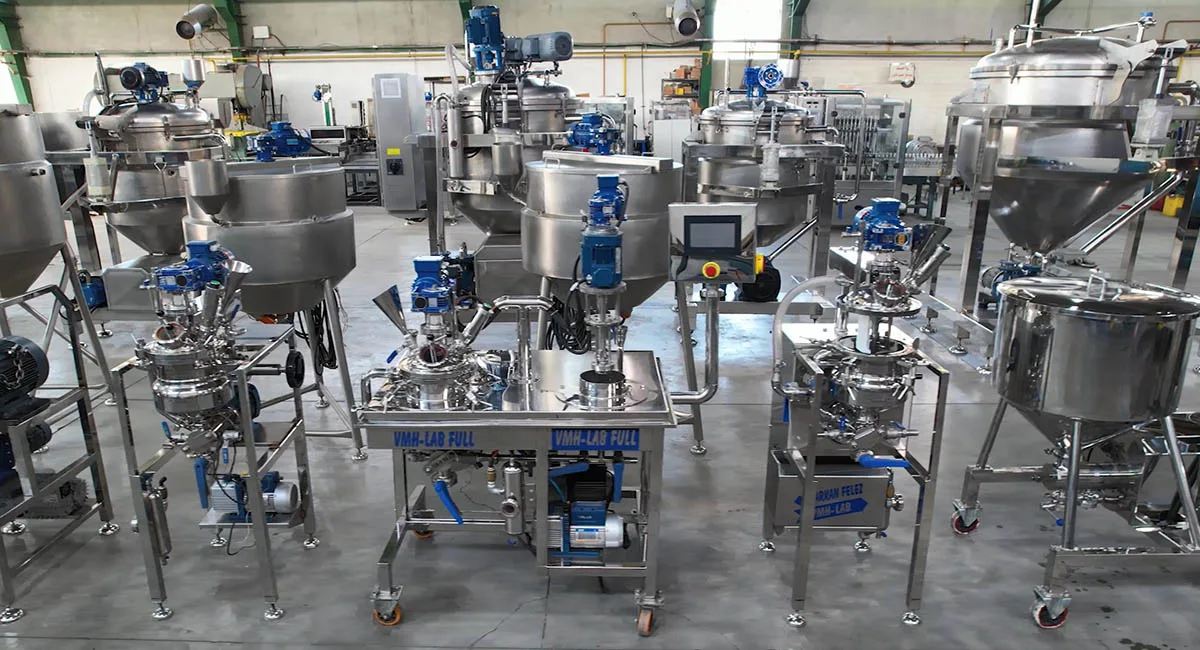
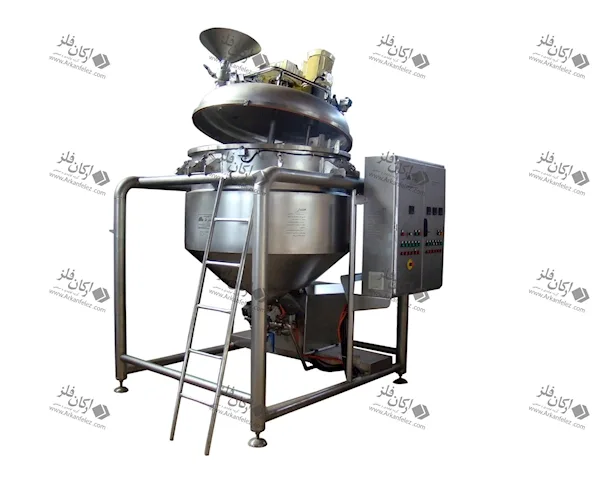
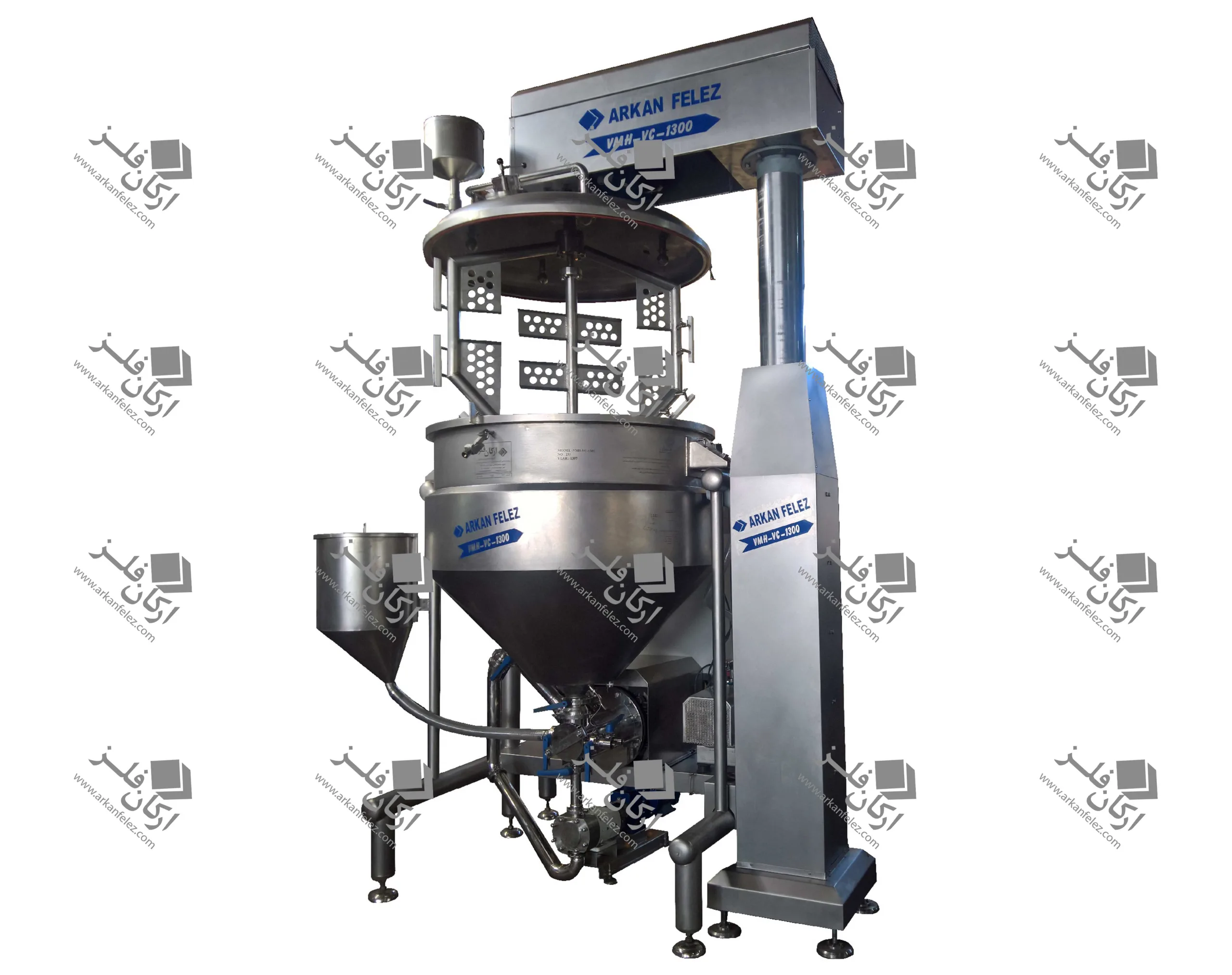
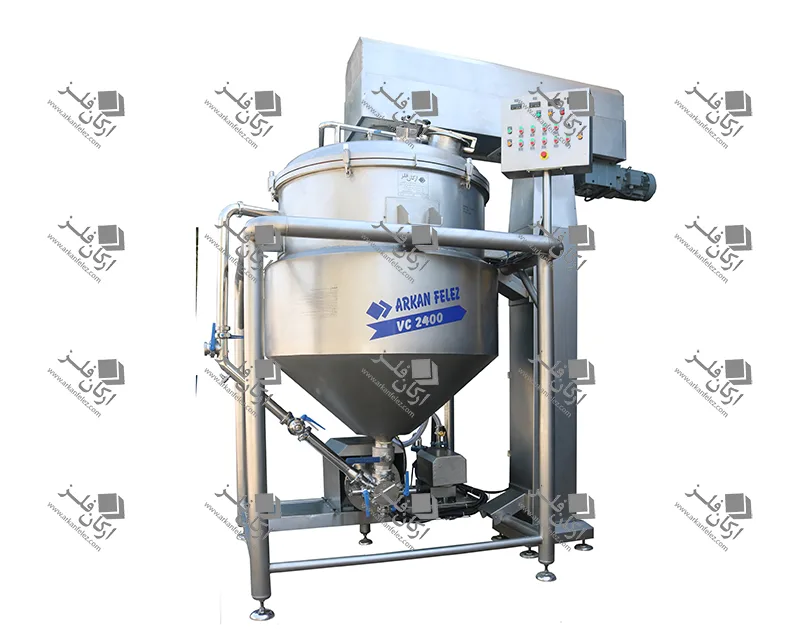
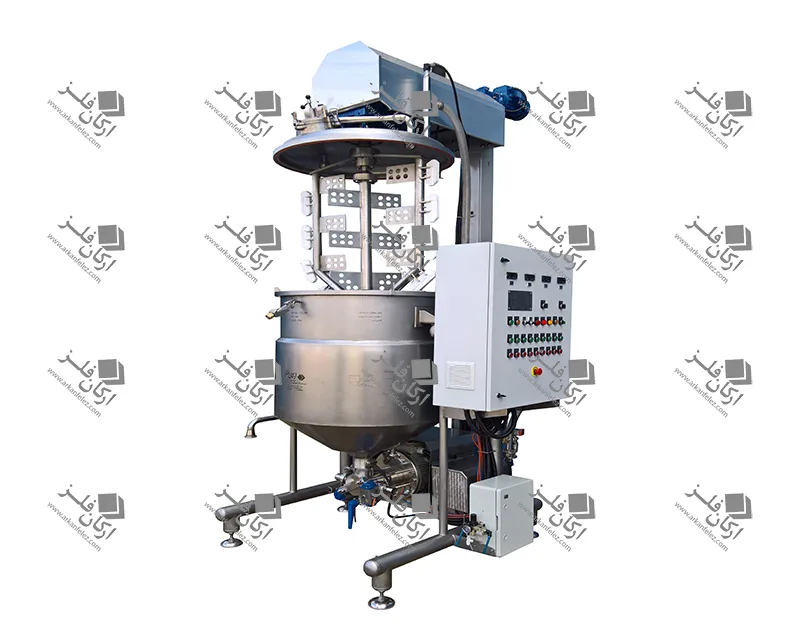
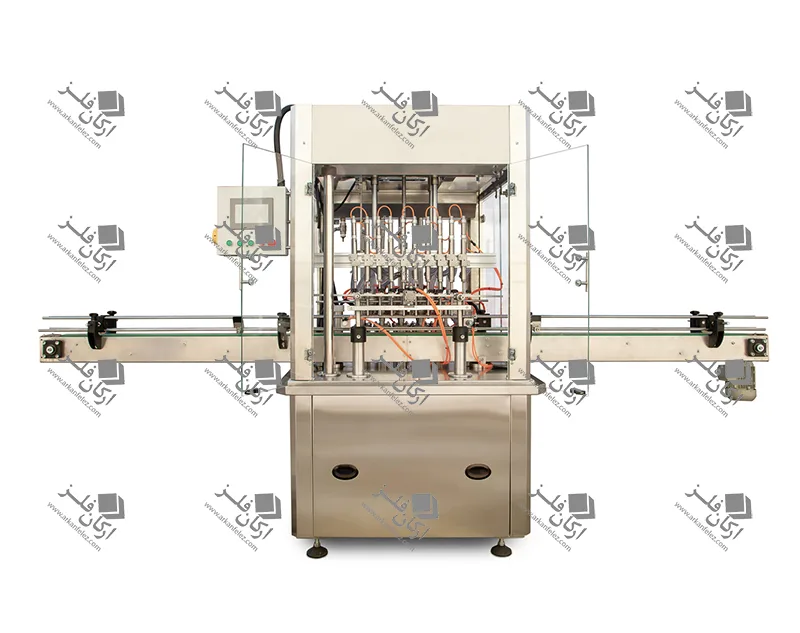
Introduction
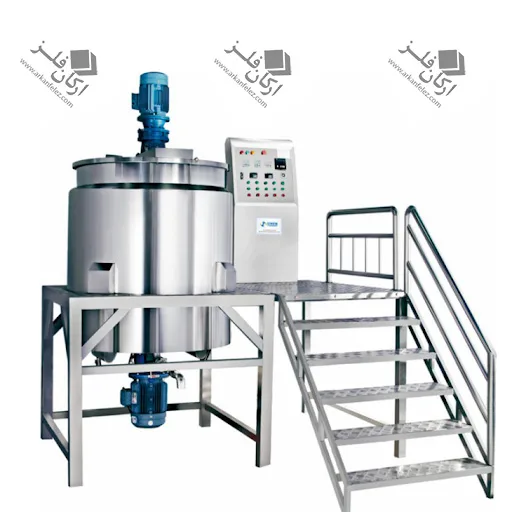
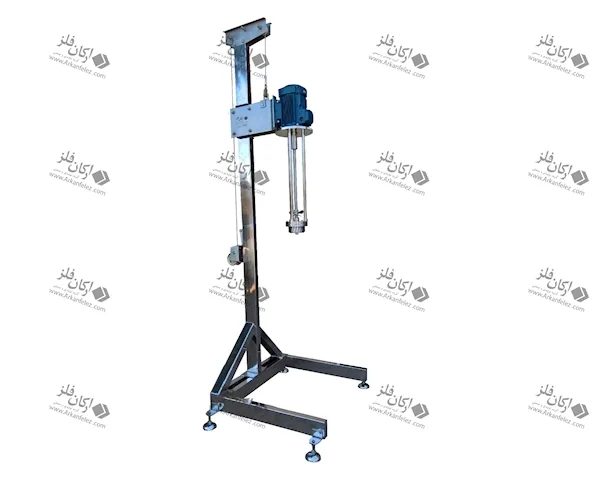
A homogenizer is an important tool in various industries such as the food, pharmaceutical, chemical and cosmetic industries, which is used to create a uniform mixture of liquids or different materials. The main function of this device is to create high pressure on the materials, which causes the division of large particles into fine and homogeneous particles. This process causes the materials to be evenly distributed among each other and improves the quality of the final product.
Homogenizers come in different types, but they are mostly divided into two categories: mechanical homogenizers and ultrasonic homogenizers. In mechanical homogenizers, a high-pressure pump is usually used to pass the liquid through tiny holes or nozzles, which causes the particles to break and divide. In the ultrasonic type, high-frequency sound waves are used to create pressure and tension in liquids.
The homogenizer is especially used in the production of products such as milk, cosmetic creams, sauces and medicines. In the food industry, a homogenizer improves the taste and consistency of products. In the pharmaceutical industry, this device can help improve the breakdown and absorption of suspended drugs. In addition, the use of a homogenizer in the production process of chemicals and dyes also plays an important role in the quality and durability of products. Homogenizers help increase production speed and reduce operating costs and are recognized as an essential tool in many industries.
Application of the homogenizer device
The homogenizer device has numerous applications in various industries that improve the quality and efficiency of products. This device is mainly used to create a uniform mixture of liquids or suspended substances in liquids and plays a fundamental role in the food, pharmaceutical, chemical, cosmetic and health industries and even in some environmental industries.
In the food industry, a homogenizer is used to produce products such as milk, sauces, jams, various drinks and even ice cream. This device improves the taste, consistency, and stability of food products by creating finer and more uniform particles. For example, in milk production, a homogenizer makes the fat and liquid mixture in milk uniform, which prevents the separation of fat from the liquid and increases the shelf life of the product.
In the pharmaceutical industry, a homogenizer is used to produce suspended drugs and suspensions. This device causes the drug particles to be evenly distributed in the liquid, thus improving the effectiveness of the drug. Also, in the production of skin drugs, creams, and ointments, a homogenizer creates a soft and uniform texture that is better absorbed by the skin.
In the chemical industry, homogenizers are used to produce dyes, resins, and detergents. These devices divide the raw material particles into appropriate sizes so that the final product is of higher quality and more stable. Homogenizers are also used in the cosmetic and health care industries to produce creams, lotions, shampoos, and other skin and hair care products. The use of a homogenizer in this industry creates a uniform and effective texture in the products that perform better in skin and hair care.
Types of Homogenizers
Types of homogenizers include ultrasonic homogenizers, high-pressure homogenizers, bead mill homogenizers, and rotor-stator homogenizers, which are explained below:
Ultrasonic Homogenizer
Ultrasonic homogenizers are a type of homogenizer used to break down and disperse particles in liquids. They operate by using very high-frequency sound waves (usually above 20 kHz). The sound waves generated by a transducer are transmitted into the liquid and create pressure and tension in it. This pressure and tension causes the large particles to break down into smaller, more uniform particles, which improves the quality of the final product.
This process uses a phenomenon called bubble reduction. When ultrasonic waves enter a liquid, bubbles are formed inside the liquid, which release a lot of energy when the bubbles burst. This explosion of bubbles causes large particles to break into smaller, more dispersed particles. This technique produces excellent results, especially in short times and with less energy consumption than other methods.
Ultrasonic homogenizers are used in many industries. In the food industry, this device helps to improve the composition of materials such as sauces, drinks and ice creams. Also, in the pharmaceutical industry, for the production of suspensions and suspended drugs, ultrasonic homogenizers play an important role in the uniformity and effectiveness of drugs. In the chemical and cosmetic industries, this device is also used to produce high-quality products with uniform textures. This type of homogenizer also has advantages such as reduced process time and low maintenance requirements, which make it an efficient and economical choice for many industries.

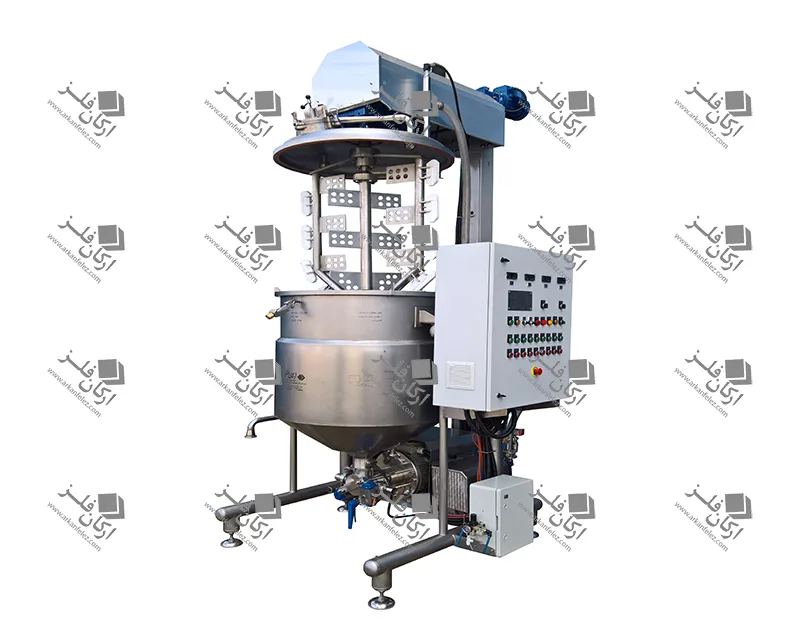
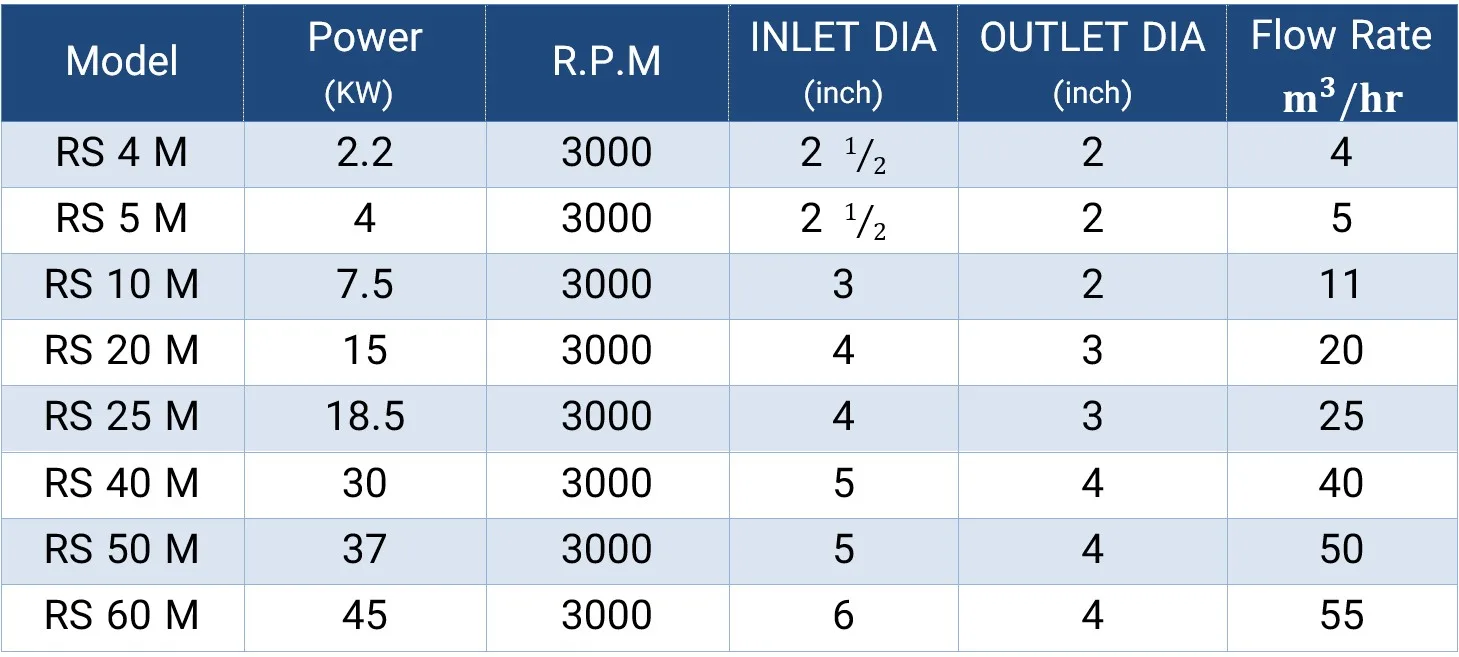
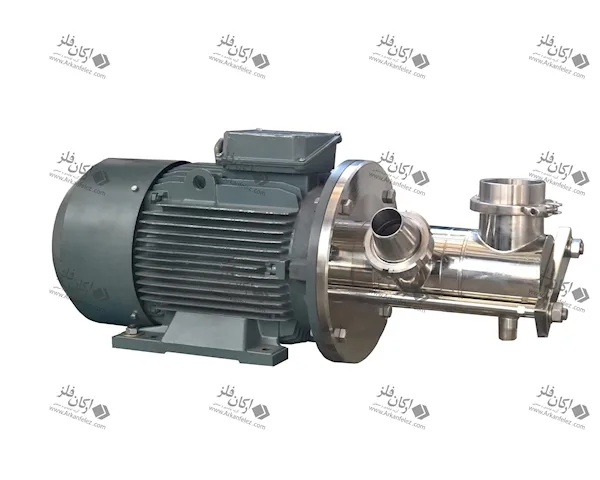
High Pressure Homogenizer
A high pressure homogenizer is one of the important types of homogenizer devices used in various industries to create a uniform mixture and divide particles into smaller particles. In this type of device, liquid passes through small nozzles or special filters under very high pressure. This high pressure causes large particles to break and become smaller and more uniform particles, which improves the quality and stability of the final product.
The homogenization process in these devices is that the liquid first enters the device and is subjected to high pressure. Then the liquid passes through nozzles with very small holes. This passage through the nozzles creates fast and powerful currents in the liquid, and in the same way, particles and substances suspended in the liquid are divided into smaller sizes. In this way, the composition of the materials in the liquid becomes uniform and no particles of the material are separated from other materials.
High pressure homogenizers are widely used in the food industry. For example, in milk production, a homogenizer homogenizes the fat in milk to prevent its separation and improve the shelf life and quality of the product. In the pharmaceutical industry, this device is also used to produce suspensions and suspended drugs so that the drug is evenly distributed in the liquid and its effectiveness is maximized. In the chemical and cosmetic industries, high-pressure homogenizers are also used to produce paints, resins, detergents, and cosmetic and hygiene products. These devices have a great impact on improving the performance and durability of products by providing a uniform and high-quality product.
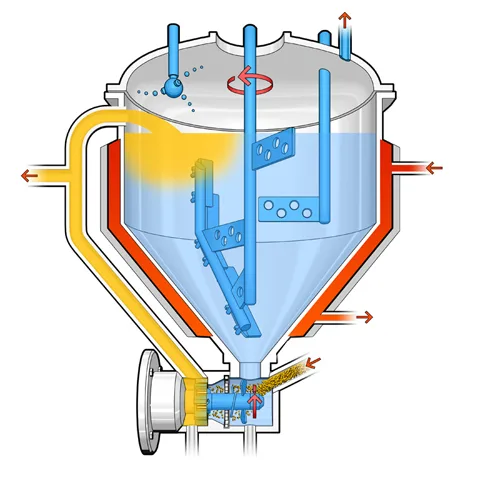
Bead mill homogenizer
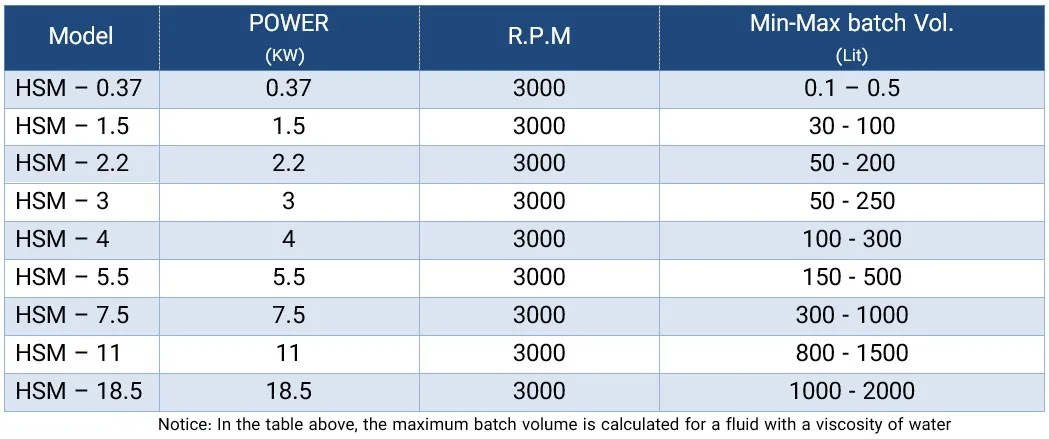
Bead mill homogenizer is a type of homogenizer used to crush and homogenize particles in liquids. This device is mainly used in the chemical, pharmaceutical, food and cosmetic industries. In a bead mill homogenizer, the homogenization process is carried out using small balls, usually made of glass, ceramic or stainless steel, which are placed inside a chamber containing liquid. These balls move back and forth, converting larger particles into smaller particles, creating a uniform mixture.
The operation of a bead mill is such that the liquid enters the chamber along with solid particles or suspended materials. Then the small balls move inside the chamber and, by colliding with larger particles, crush them and convert them into smaller sizes. This process is carried out by the force of friction and impact between the balls and the particles. In this way, the particles are dispersed uniformly and very finely in the liquid.
The beet mill is widely used in various industries due to its ability to crush particles to very fine sizes. In the food industry, it is used to produce sauces, jams, suspended drinks and ice cream. In the pharmaceutical industry, the beet mill is used to produce suspensions and suspended drugs that require uniform dispersion. Also, in the cosmetic and health industries, the beet mill is used to produce creams, lotions and skin and hair care products. This type of homogenizer is effective in producing high-quality products with uniformity in texture and composition of materials due to its high ability to crush particles.
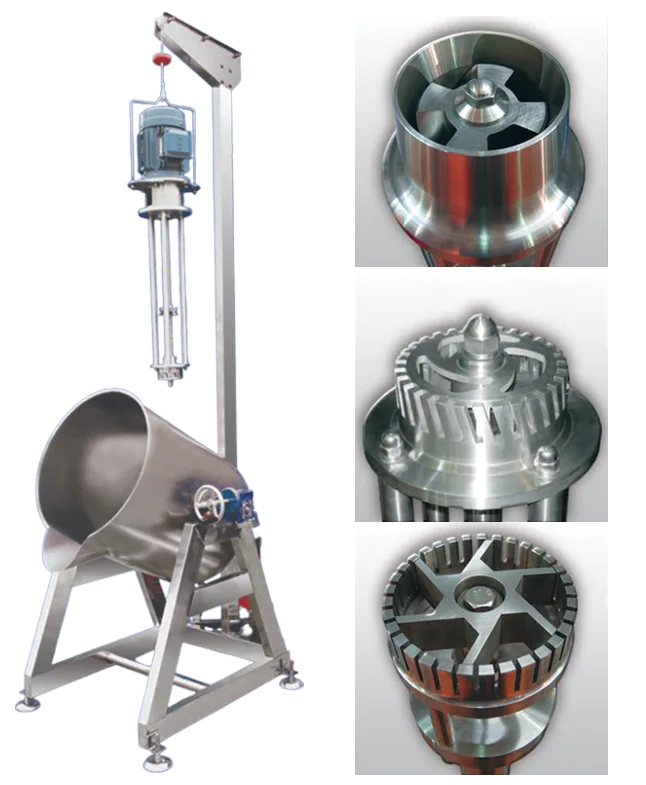

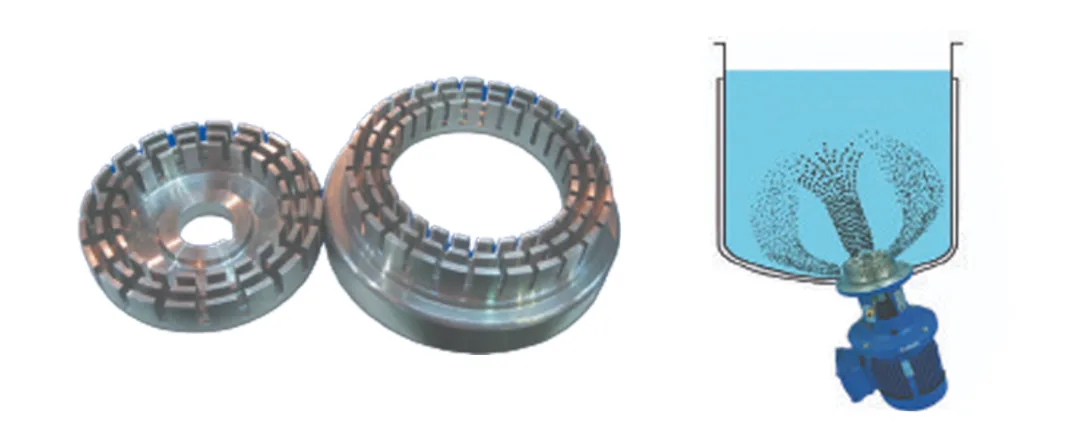
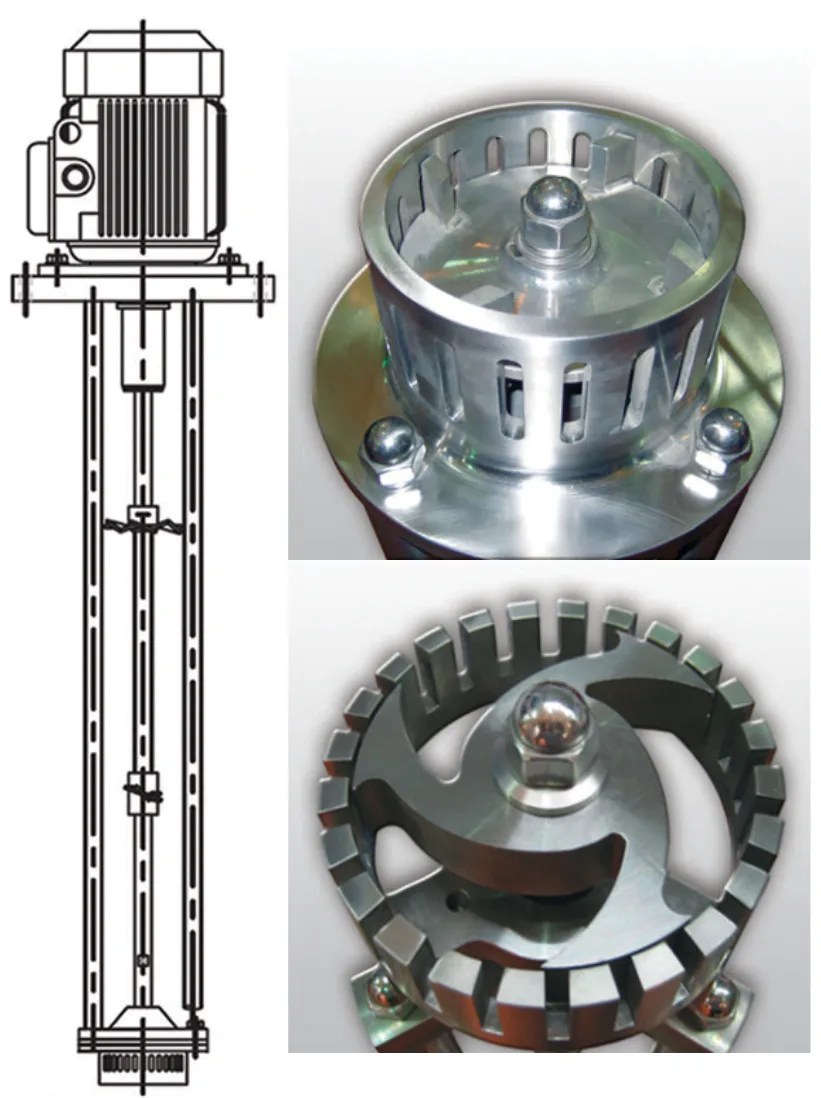
Rotor Stator Homogenizer
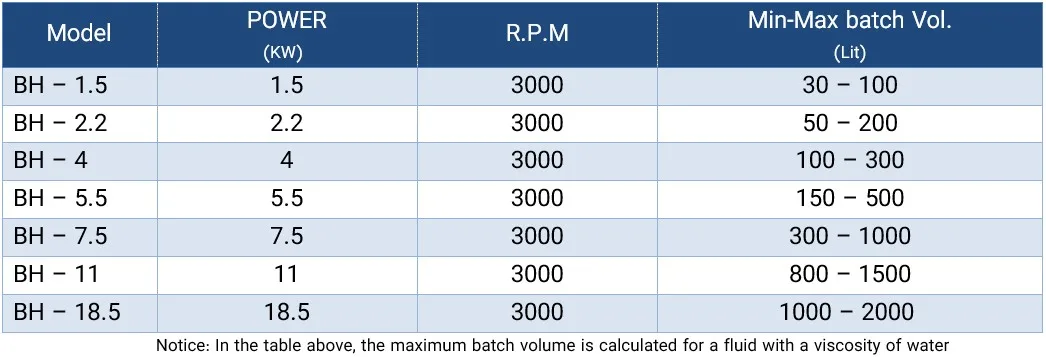
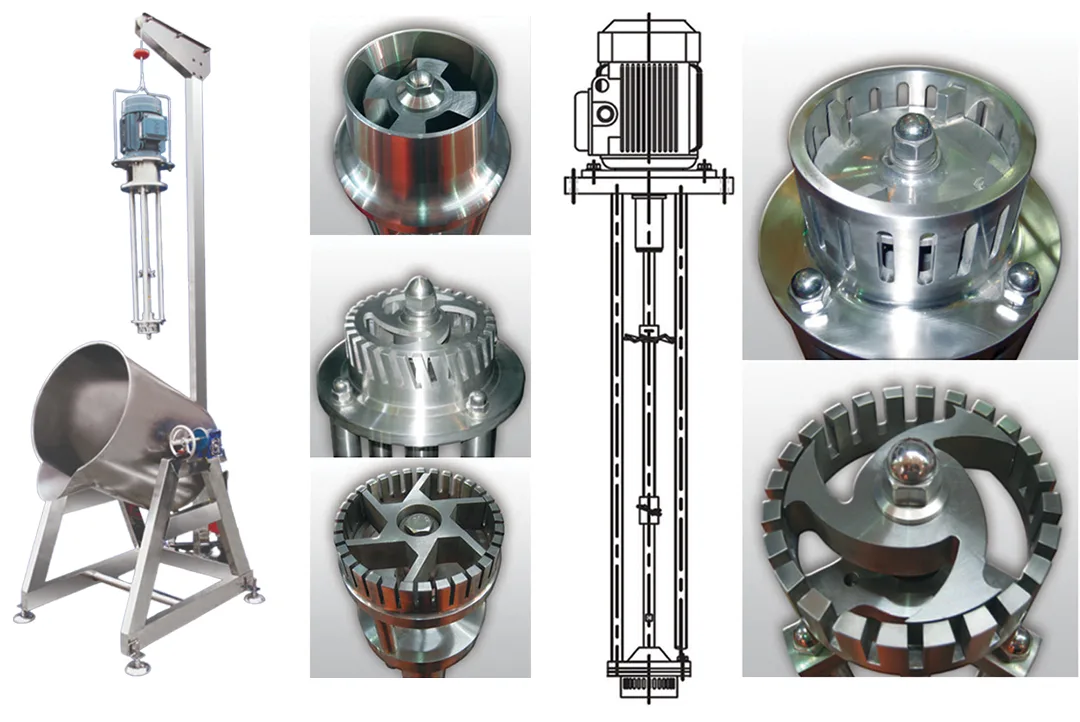
Rotor Stator Homogenizer is a type of homogenizer used to create uniform mixtures of different materials in liquids. This device is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, chemical and cosmetic industries. The principle of operation of this device is based on the use of a rotating rotor and a fixed stator, which together produce a strong shear force to crush and homogenize particles of suspended materials in the liquid.
In this device, the liquid enters a chamber that includes a rotor and a stator. The rotor, which usually rotates at high speed, draws the liquid into the stator. The stator, which is fixed in place, creates shear and tensile forces by colliding with the liquid flow and its particles, which causes the particles to be crushed and dispersed evenly. This process leads to a reduction in particle size and better mixing of materials.
Rotor-stator homogenizers are used in many manufacturing and industrial processes due to their simple and efficient design. In the food industry, this device is used to produce products such as sauces, drinks, jams and ice cream to evenly disperse fat particles and other substances in the liquid. In the pharmaceutical industry, this type of homogenizer is also used to produce suspensions and suspended drugs that require uniformity. One of the advantages of the rotor-stator homogenizer is the high speed of the homogenization process and its ease of use and maintenance. This device is usually suitable for small to medium volumes and has a lower cost than other types of homogenizers.

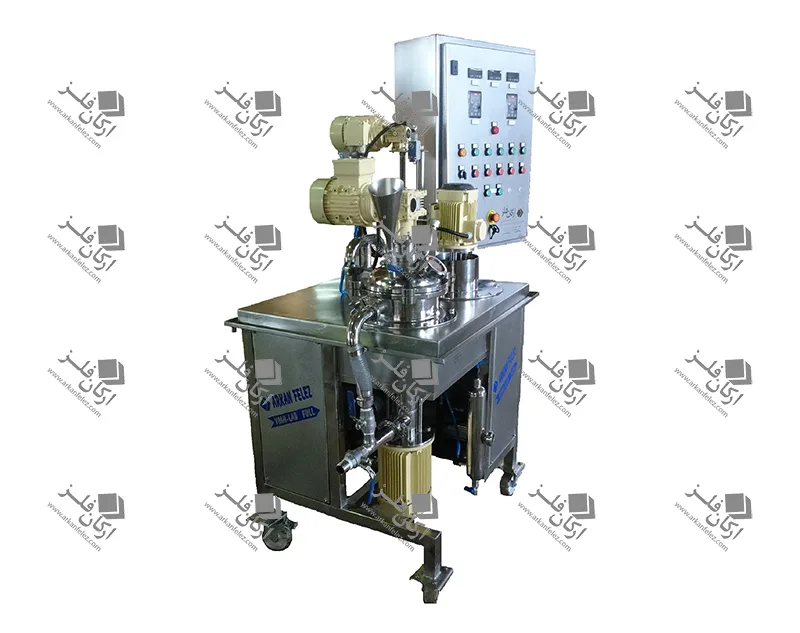
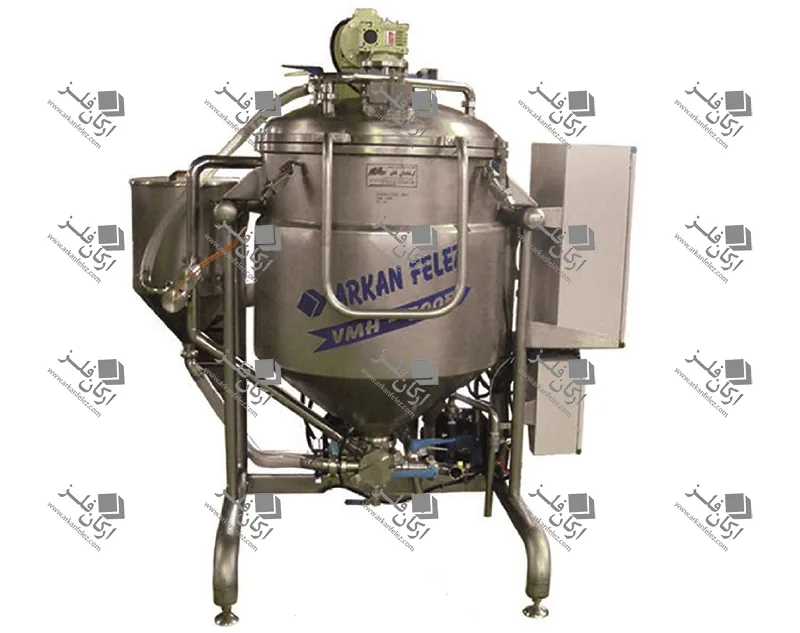
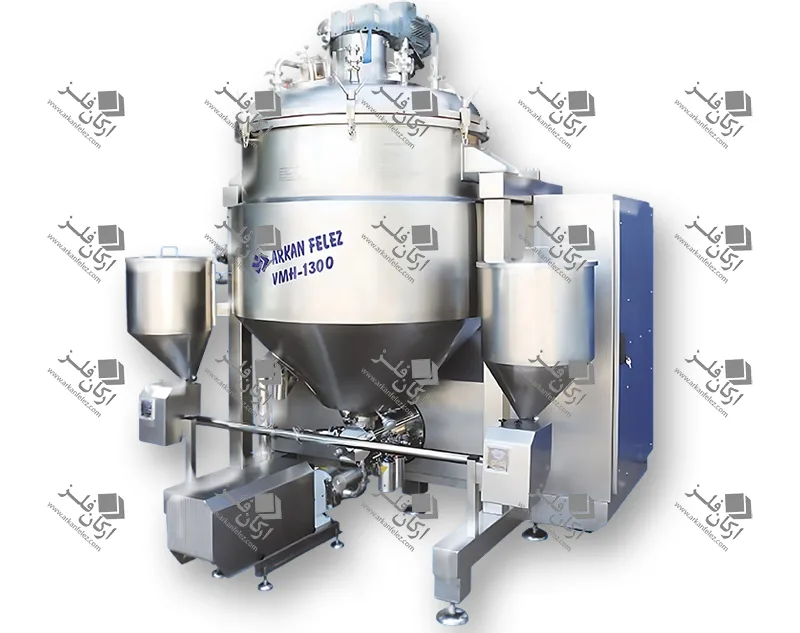
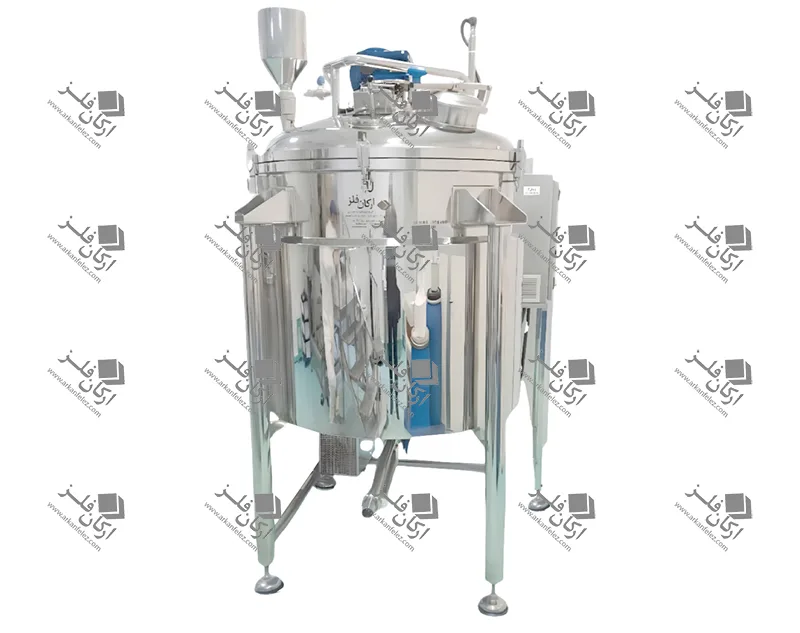
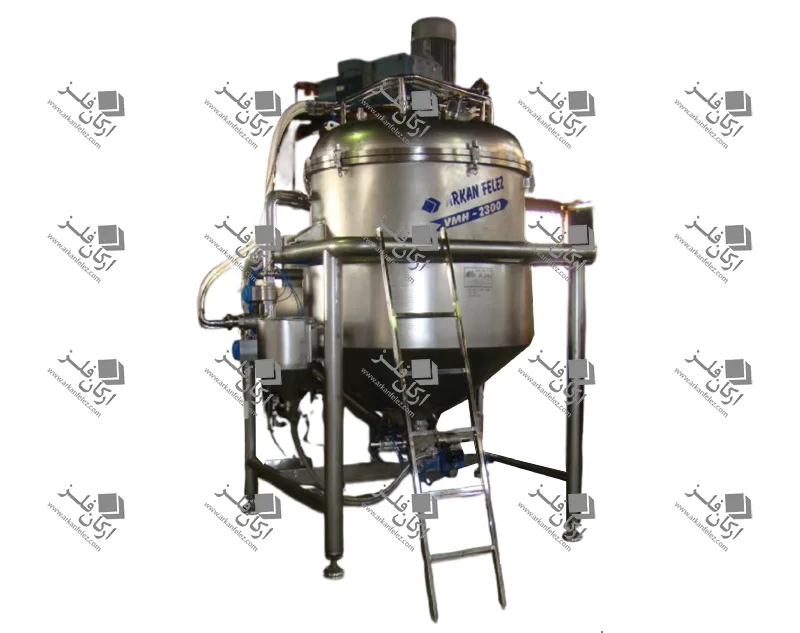
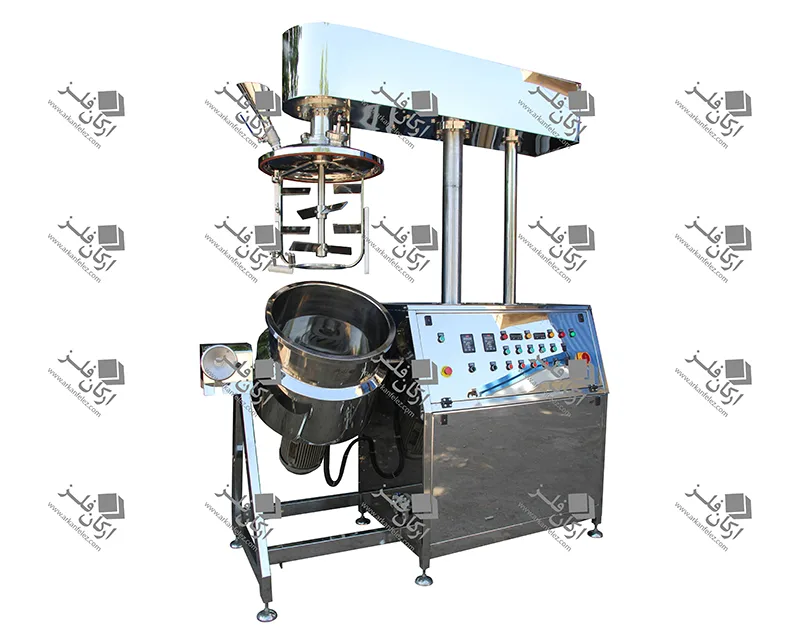
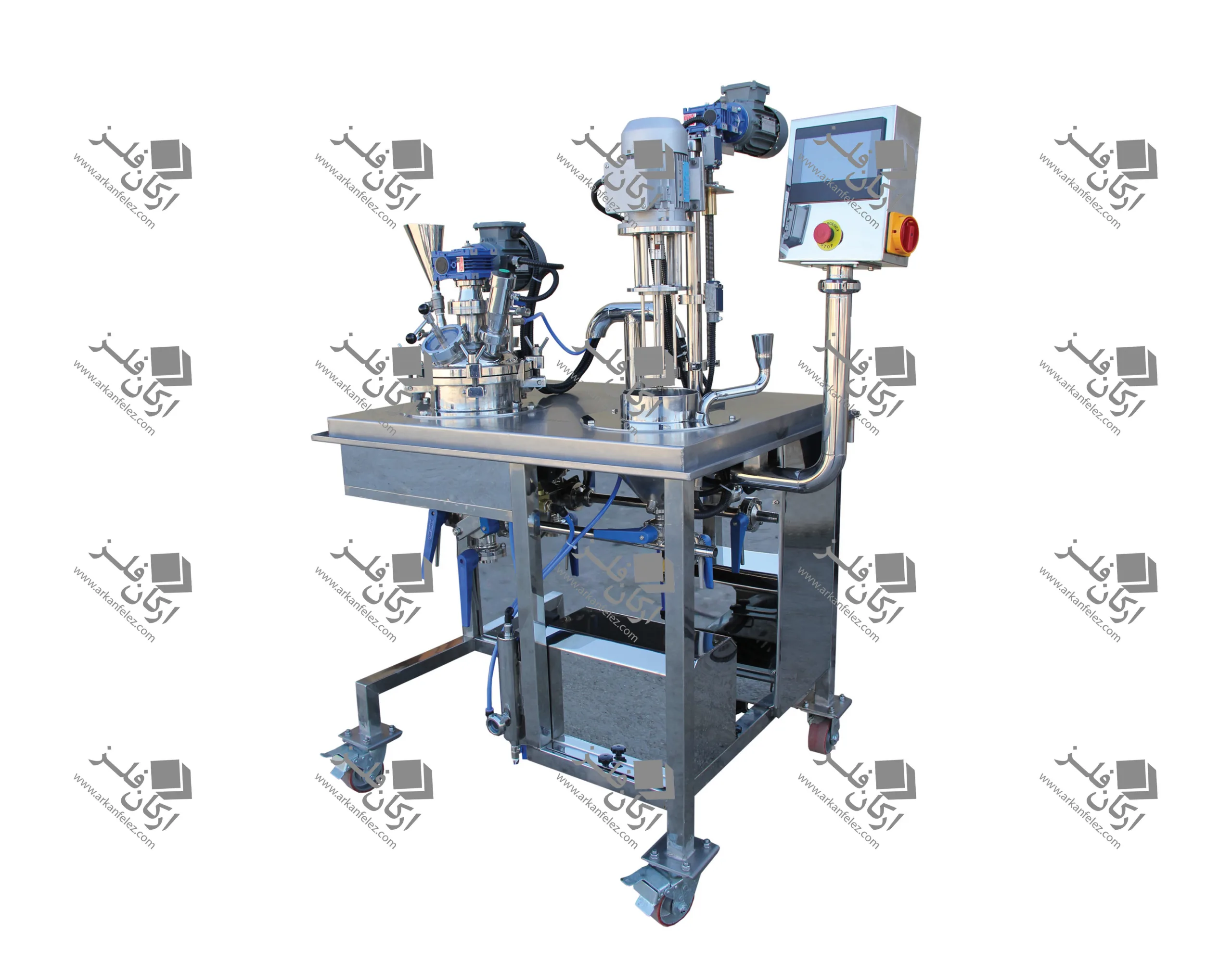
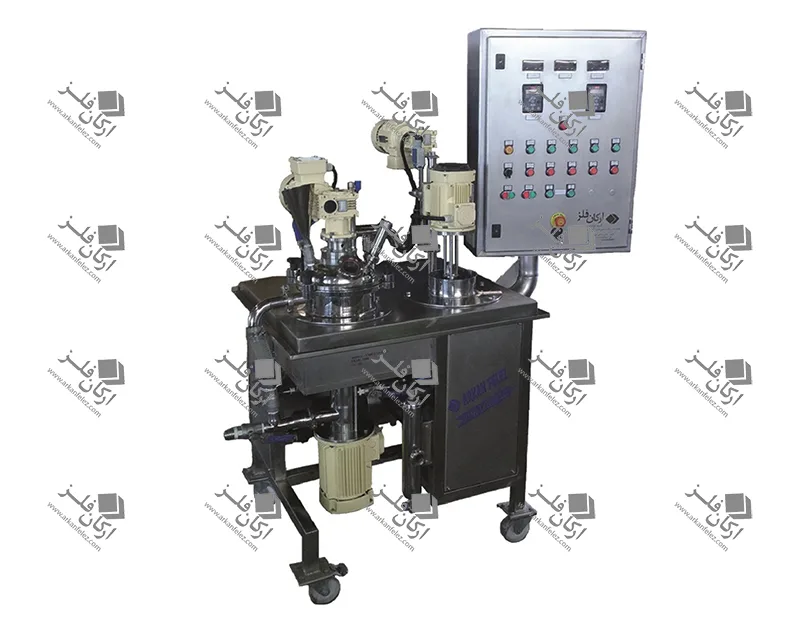
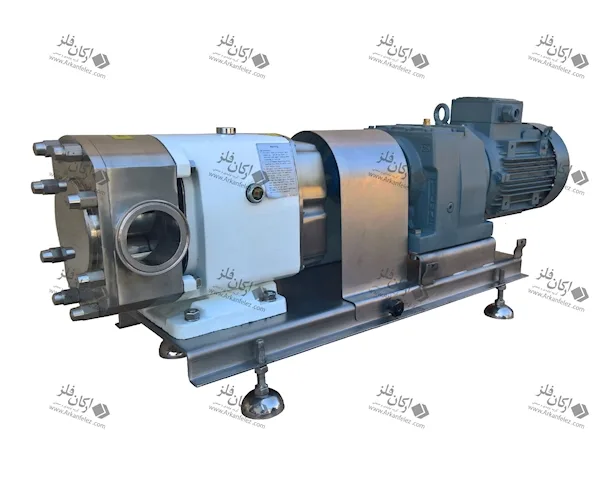
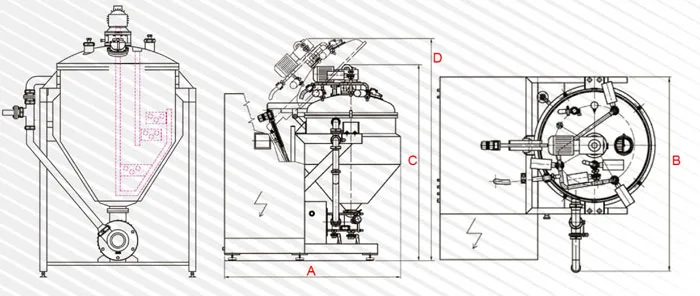
Different Parts of a Homogenizer
A homogenizer device is made up of different parts, each of which plays a specific role in the homogenization process and the production of the final product. Here are the most important parts of a homogenizer:
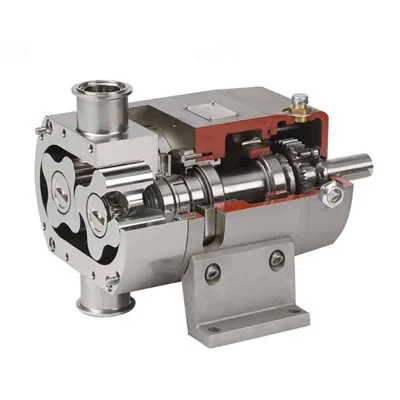
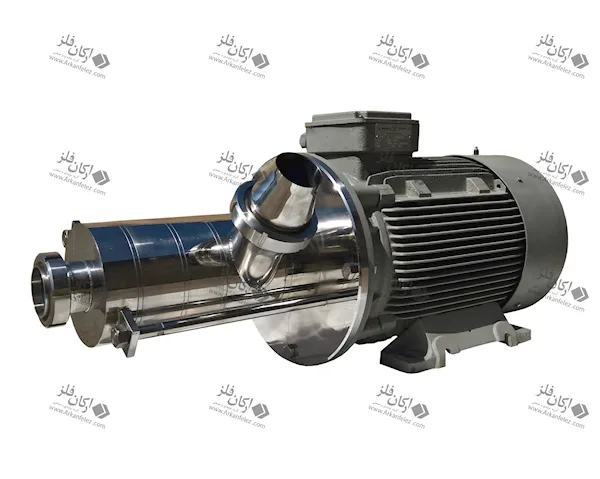
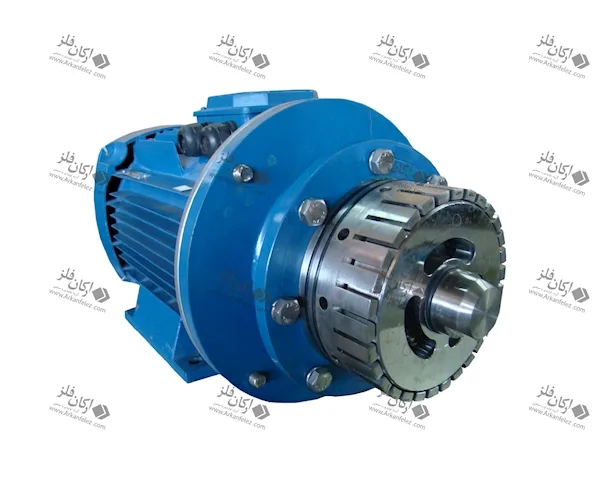
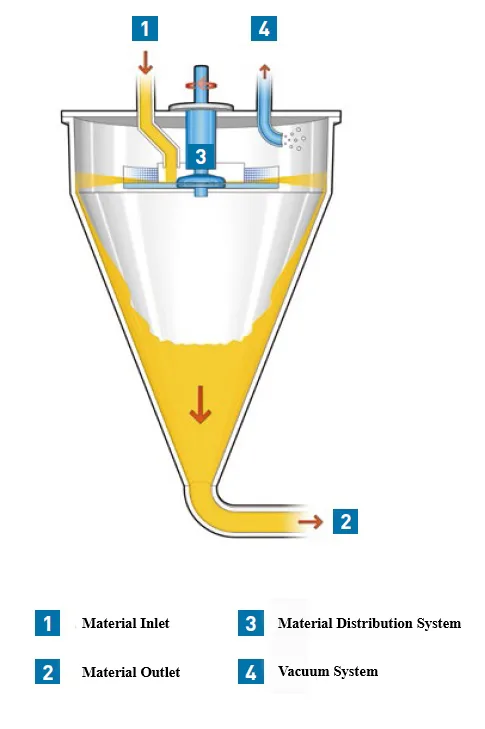
Inlet Pump: This part is responsible for transporting the liquid or material into the homogenizer. The inlet pump is usually designed to introduce the liquid flow into the system at the appropriate pressure so that the homogenization process can begin properly.
Rotor and Stator System: One of the main parts of the homogenizer is the one that performs the actual homogenization process. The rotor (which rotates) directs the liquid towards the stator (which is stationary). The stator creates high shear force to crush large particles and convert them into finer, more uniform particles.
Nozzles: Nozzles are used in the homogenizer to force the liquid under pressure through tiny holes. This process breaks the particles and mixes them better. In some models, the nozzles are designed in multiples to create better homogenization.
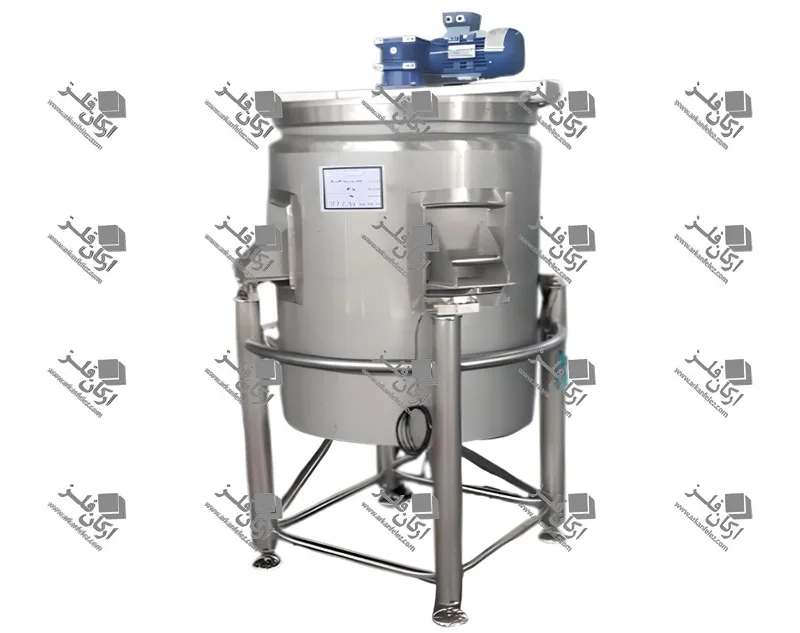
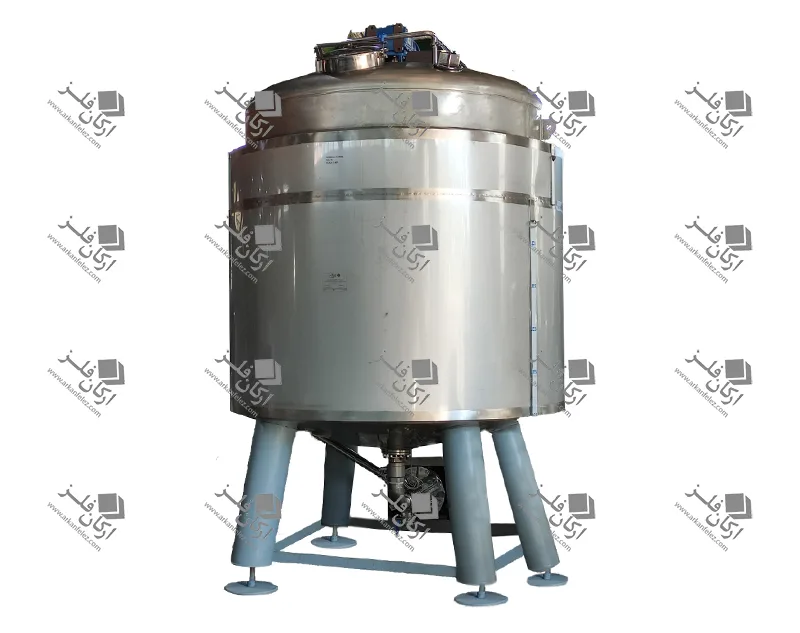
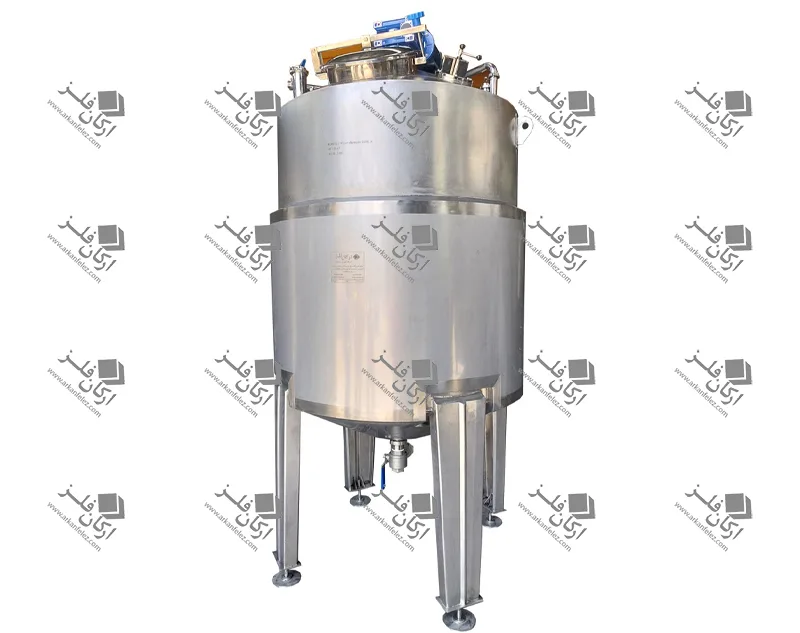
Chamber: The chamber or tank is where the liquid or raw materials enter and the homogenization process takes place inside it. In this tank, the liquid is subjected to high pressure and shear force to reduce the particles to smaller sizes.
Pressure Control System: This system is designed to regulate the pressure required for the homogenization process. The appropriate pressure is different for each type of material and this system ensures that the pressure remains within a certain range to achieve the best result.
Outlet: After the liquid has undergone the homogenization process, it is discharged through the outlet of the device. This homogenized liquid is ready to be used in the next stages of production.
All of these departments work together to ensure the homogenization process is carried out in the best possible way and to produce a final product with high quality and excellent uniformity.
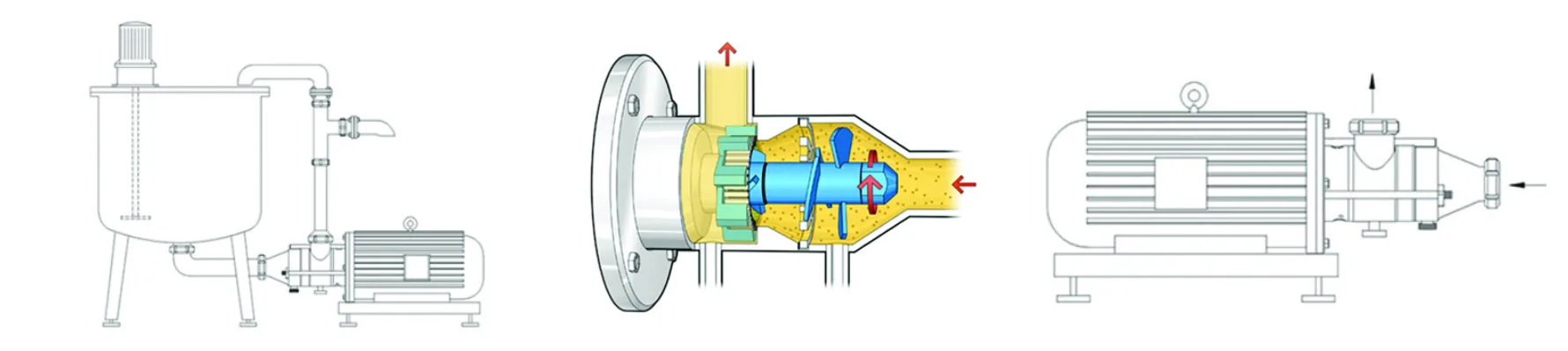
How does a homogenizer work?
The homogenizer works by applying high pressure and shear to break up and disperse large particles in liquids. It is mainly used in the food, pharmaceutical, chemical and cosmetic industries to produce high-quality, uniform products. But how exactly does this process work?
First, the raw materials, which can be liquids or suspended solids, are fed into the machine through an inlet pump. The pump directs the liquid into the homogenizer chamber and puts it under high pressure. The liquid then enters the rotor and stator sections. In this section, the rotating rotor directs the liquid towards the stationary stator. The stator creates a strong shear force that breaks large particles into smaller particles. This shear force creates a uniform and dense mixture of liquid and particles. In some types of homogenizers, the liquid passes through fine nozzles. These nozzles exert high pressure on the liquid, and thus, the particles are divided into smaller and more uniform sizes. In ultrasonic homogenizers, high-frequency sound waves are used to create pressure and tension in liquids, which also helps in the breakdown and dispersion of particles.
After the materials have undergone the homogenization process, the liquid is removed from the device and is ready for use or packaging. At this stage, the particles have become small enough that they no longer separate or precipitate, and the final product is uniform and of high quality. As a result, the homogenizer uses high pressure and shear force to crush the material particles, creating a uniform and stable mixture that is required in many industries.
How to work with a homogenizer
How to work with a homogenizer generally includes specific steps that must be followed carefully to achieve the desired result in the homogenization process. These steps include preparing the device, setting the parameters, loading the materials, and performing the homogenization process. The first step in working with a homogenizer is preparing the device. Before starting work, the device must be thoroughly cleaned to prevent any contamination or residue from previous materials. After that, all parts of the device such as the pump, rotor, stator, nozzles, and pressure system must be checked and their health must be ensured.
In the next step, the raw materials, which can include liquids or materials suspended in liquids, are introduced into the device. Usually, liquids are transferred into the homogenizer chamber through a pump. The pressure and speed of the pump must be carefully adjusted to achieve the desired result in the homogenization process. To adjust these parameters, the appropriate pressure and speed must be selected according to the type of material to be homogenized.
After the settings, the homogenization process begins. In this step, the liquid passes through the fine nozzles or the rotor and stator system under high pressure. This passage causes the material particles to be divided into smaller sizes and dispersed evenly in the liquid. Depending on the type of homogenizer, such as high-pressure, ultrasonic or rotor-stator homogenizer, this process can be carried out in different ways. After the process is complete, the homogenized liquid is discharged from the device. Finally, the final product is ready for use or packaging. To ensure quality, tests may be required to check the uniformity and size of the particles. Also, after each use, the device must be thoroughly cleaned and ready for reuse.

Homogenizer Uses in Dairy Industries
Homogenizers are very important in dairy industries and play a key role in improving the quality of dairy products. One of the main uses of homogenizers in this industry is the process of homogenizing milk. This process means making the fat and liquid composition of milk uniform to prevent fat from separating from milk. In the homogenization process, milk passes through fine nozzles under high pressure, which causes the fat particles to be divided into smaller and more uniform particles. This action makes the milk homogeneous and uniform and prevents the formation of fat layers on the surface of the milk. Homogenizers are also used in the production of other dairy products such as butter, yogurt, cheese and ice cream. In butter production, the homogenizer helps reduce the size of fat particles so that the process of separating butter from curd is easier and more effective. In yogurt production, the homogenizer helps to evenly distribute beneficial bacteria inside the milk, leading to improved taste and texture of the final product.
In ice cream production, a homogenizer helps to evenly distribute fat and liquids among other ingredients such as milk, cream, and sugar, which helps improve the soft and creamy texture of ice cream. The homogenizer also reduces the size of ice crystals in ice cream, which helps improve the taste and prevent unpleasant texture in ice cream. Finally, using a homogenizer in the dairy industry, in addition to improving the quality and taste of products, increases their shelf life and stability. These devices also help increase productivity and reduce material waste.
Important points when using a homogenizer
When using a homogenizer, observing some important points can help increase the efficiency of the device, improve the quality of the final product, and prevent technical problems. Below are some basic points that should be considered when using a homogenizer:
Correctly adjust the pressure and speed: One of the most important points is adjusting the pressure and speed of the device. Excessive pressure can damage the machine or produce particles that are too fine, while low pressure will cause incomplete homogenization. Also, the appropriate speed setting for the rotor and stator is different for each type of material.
Raw material preparation: Raw materials such as milk, liquids or suspended materials must be properly prepared before the homogenization process begins. For example, the materials must reach the appropriate temperature for effective homogenization.
Machine cleanliness: The homogenizer must be thoroughly cleaned after each use. Residual materials from the previous process can affect the quality of the final product. Proper cleaning of the machine from contaminants and material residues extends the life of the machine and prevents cross-contamination.
Machine health check: All parts of the machine such as pumps, nozzles, rotor and stator should be checked before starting to ensure that there is no damage or failure. In particular, the nozzles must be clean and unclogged so that the homogenization process can be carried out optimally.
Temperature control: In some cases, an increase in temperature during homogenization can lead to the decomposition of sensitive substances or change the taste and texture of the final product. Therefore, temperature control and the use of cooling systems when necessary are of great importance.
Follow production instructions: Each type of homogenizer may have its own instructions for best performance. Following these instructions, including the appropriate time and pressure for the process, will help achieve better results.
Following these tips when using a homogenizer will not only help improve the quality of the final product but also extend the useful life of the device.
In which industries is a homogenizer used?
A homogenizer is used in many industries to improve the quality and uniformity of products. This device divides material particles into smaller sizes by creating high shear force and pressure and causes them to be uniformly mixed in liquids. Here are some important industries that use a homogenizer:
Food industries: One of the main applications of a homogenizer is in the food industry. In the production of products such as milk, sauces, jams, ice cream, beverages and other liquid foods, a homogenizer is used to prevent the separation of substances and fats. The homogenizer causes fat particles in liquids to be divided into smaller sizes and the final product is uniform and of high quality.
Pharmaceutical industry: Homogenizers play a vital role in the production of liquid medicines and suspensions. This device helps to evenly distribute active pharmaceutical ingredients in liquids and improves the effectiveness and stability of the drug. Homogenizers are also used in the production of pharmaceutical emulsions and creams.
Chemical industry: In the production of paints, resins, detergents and other chemical compounds, a homogenizer is used to ensure the uniformity and stability of products. This device is important for the uniform dispersion of material particles in liquids and preventing their sedimentation.
Cosmetics and health industry: In the production of creams, lotions, gels and other skin care products, a homogenizer is used to obtain a uniform texture and long-term shelf life. This device helps in the uniform distribution of active ingredients and oils in the products.
Oil and gas industry: In some refining and production processes of petroleum products, a homogenizer is used to mix various materials such as additives and liquids. This increases the quality and stability of petroleum products.
Agricultural industry: In the production of pesticides and liquid fertilizers, a homogenizer is used to evenly distribute chemicals in the liquid. This helps increase the efficiency and performance of agricultural products.
Overall, homogenizers are used in various industries that require uniformity in liquid materials and have a great impact on improving the quality and stability of final products.